What disease is this?
Causes of osteochondrosis
Muscle spasms and malnutrition
- Make monotonous movements;
- Working in physically demanding jobs;
- Spend a lot of time motionless.
blood supply problems
Lack of fluid in the body
metabolic diseases
stressful situations
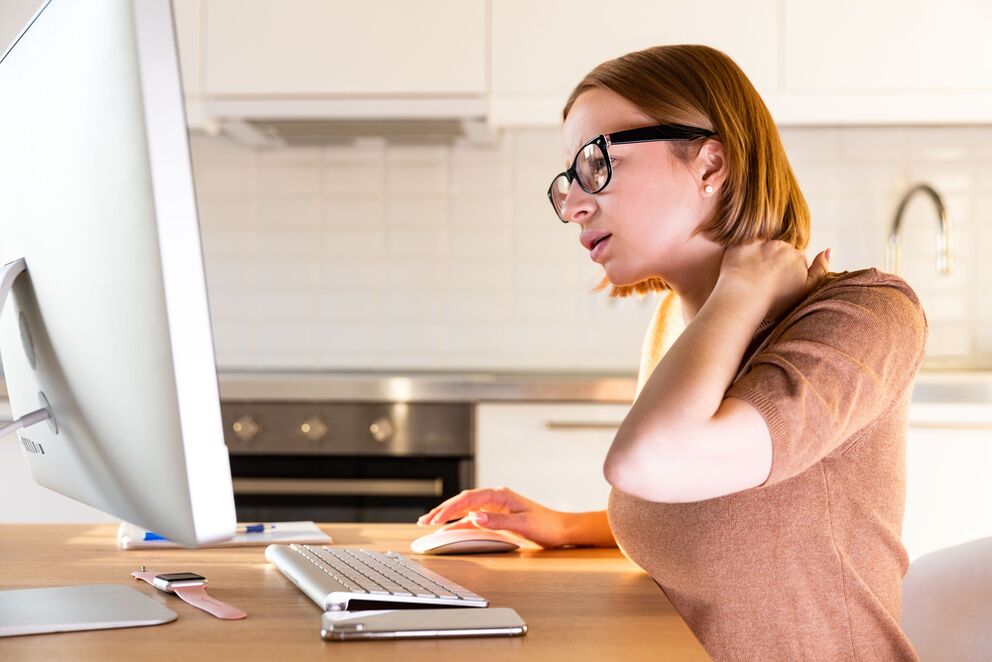

risk factors
- Genetic background.
- Nervousness.
- Sustained physical activity.
- Sedentary work, sedentary lifestyle.
- Passion for junk food, being overweight.
- Bad habits that lead to metabolic disorders in cartilage tissue.
- Disorders of the musculoskeletal system.
development stage
Phase I
second stage
The third phase
Stage 4
Classification and symptoms
cervix
- Headache, heaviness in the back of the head, dizziness;
- Tingling in the hands;
- The neck is most often under tension;
- The vertebrae click and creak when you turn your head;
- Occasionally, you may experience a sore throat or a lump in your throat;
- It is difficult to move your arm to the side or lift it due to tight neck muscles.
lumbar spine
- Limited spinal movement;
- Patients may experience hip discomfort with cramping;
- Notice dry, flaky skin on the legs, and goosebumps;
- Periodic acute stinging may occur;
- During sleep, a person cannot adopt a comfortable position because any position would make him uncomfortable.
Chest
- Band pain can become more intense if you are active;
- Tingling in the heart area;
- Feeling of fullness in armpits;
- Limit shoulder movement;
- Shortness of breath and difficulty breathing.
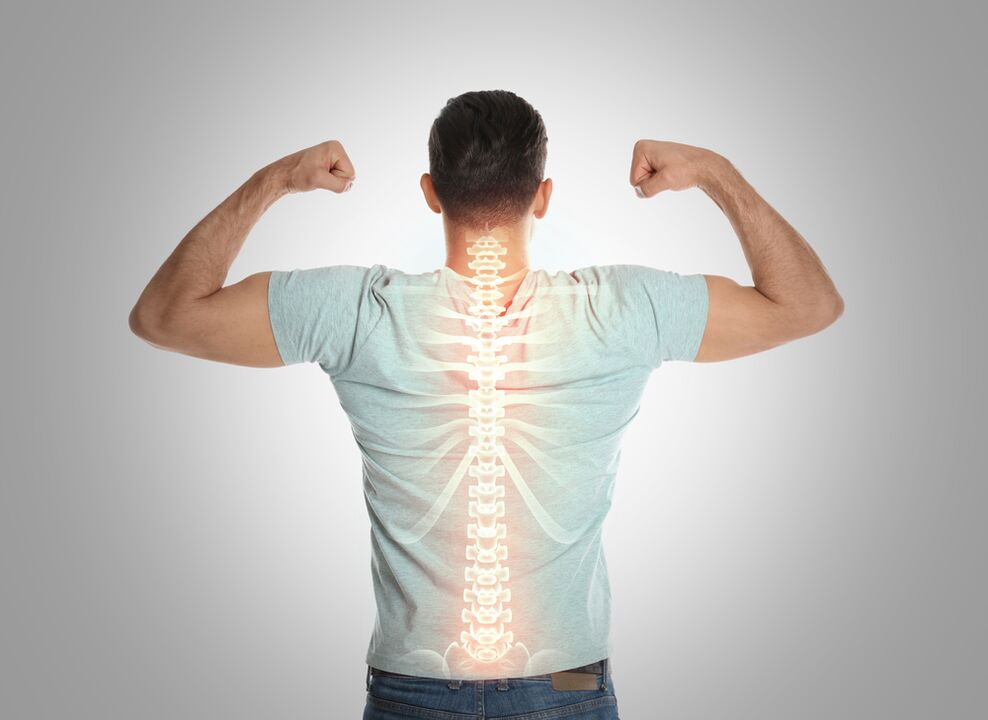
diagnosis
- Magnetic resonance imaging is the most accurate method of obtaining objective information about tissue condition.
- Spine X-ray.
- CT examination.
How is the disease treated?
- Observe bed rest during periods of worsening pain;
- avoid physical activity;
- Wear a support bra, bandages, and girdle.
drug
- nonsteroidal anti-inflammatory drugs;
- chondroprotectant;
- Muscle relaxants;
- B vitamins.
physiotherapy
massage therapy
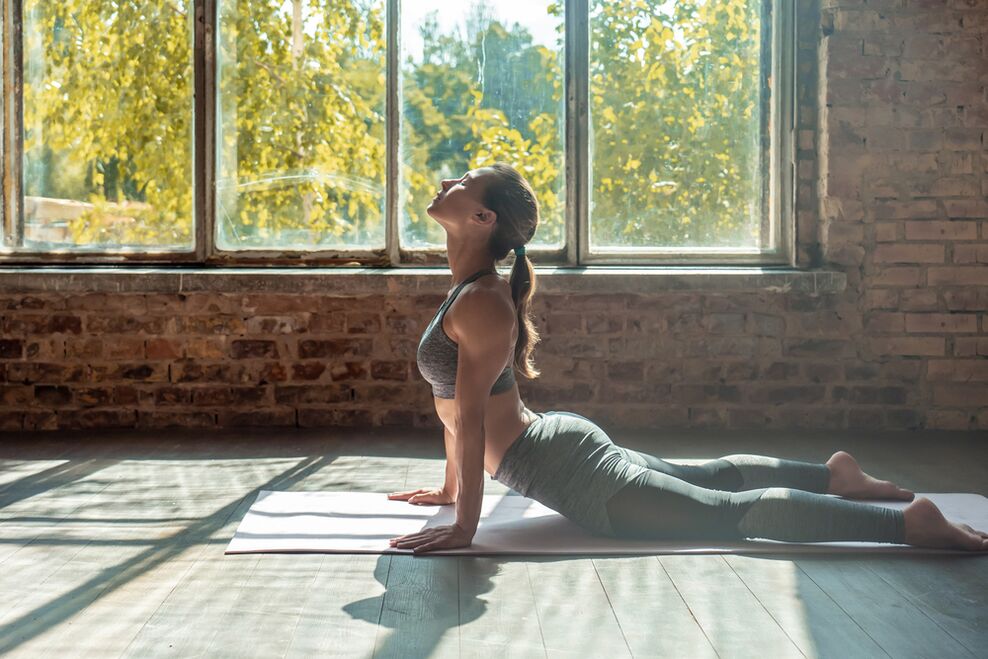

prevention
- Pay attention to your posture and don't hunch your back.
- Work out at home to keep all muscle groups toned.
- Perform exercises to relax the muscles in your back, shoulders, and neck.
- Take yoga classes and therapeutic massage sessions.
- Don't lift heavy objects, distribute the load evenly across your arms.